Introduction to Verification vs Validation
Design verification and validation are critical components of the design process when developing a medical device. It is vital to have a clear understanding of the distinctions between these two concepts and the specific requirements associated with each activity. In this post, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the FDA’s guidelines and requirements for design verification and validation in the medical device industry.
Design verification focuses on confirming that the design outputs of a medical device meet the specified design inputs. It involves a systematic and objective evaluation of the device’s design to ensure that it fulfills the intended requirements. This process encompasses various activities such as testing, analysis, inspections, and reviews, which aim to validate the design’s functionality, performance, safety, and regulatory compliance.
On the other hand, design validation goes beyond verification and aims to demonstrate that the device, when used in its intended environment and under normal conditions, meets the user needs and intended uses. Validation activities typically involve conducting clinical evaluations, performing usability studies, and gathering feedback from end-users to ensure that the device performs as expected and achieves the desired clinical outcomes.
The FDA has established specific requirements for design verification and validation to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. These requirements are outlined in various regulatory documents, including the FDA’s Quality System Regulation (QSR) and the Design Control Guidance for Medical Device Manufacturers.
For design verification, the FDA expects manufacturers to develop and execute a comprehensive verification plan that includes specific objectives, test methods, acceptance criteria, and documentation of results. The verification activities should cover all relevant aspects of the device’s design, including its components, software, packaging, labeling, and instructions for use. Manufacturers must ensure that the design verification is thorough, well-documented, and performed by qualified personnel.
In terms of design validation, the FDA emphasizes the importance of conducting validation activities throughout the entire design process. Manufacturers are required to establish and follow a validation protocol that outlines the approach, methods, acceptance criteria, and responsibilities for each validation activity. This includes conducting clinical studies, usability testing, and post-market surveillance to gather real-world data on the device’s performance, safety, and user satisfaction.
It is worth noting that design verification and validation are iterative processes that should be performed in conjunction with other design control activities. Manufacturers should document and maintain a comprehensive Design History File (DHF) that includes evidence of both verification and validation activities, along with other design control records.
By adhering to the FDA’s requirements for design verification and validation, medical device manufacturers can ensure the development of safe, effective, and compliant devices. These activities play a crucial role in mitigating risks, identifying design flaws or deficiencies, and ultimately delivering high-quality products that meet the needs of healthcare professionals and patients.
We have been extensively discussing about different topics that are related to design verification and validation, such as biocompatibility, sterilization, reprocessing of single use device, clinical evaluation.
Verification vs Validation: some definitions
Firstly, let’s start with some definitions. The definition of Design Verification and Design Validation is reported in section 820.30 of Code of Federal Regulation (CFR), at the lefters f) and g). Specifically:
- Design Verification is confirmation by objective evidence that design output meets design input.
- Design Validation means establishing by objective evidence that specifications (specified requirements) conform with user needs and intended use(s).
Design Validation
Design validation means performing specific tests on the device to demonstrate it works for end user according to its specific intended use. If for example we imagine to have a product which is only constituted by software (the so-called, SAMD, Software as Medical Device), design validation means demonstration that what we can call Global System Requirements (that include user needs) are fulfilled.
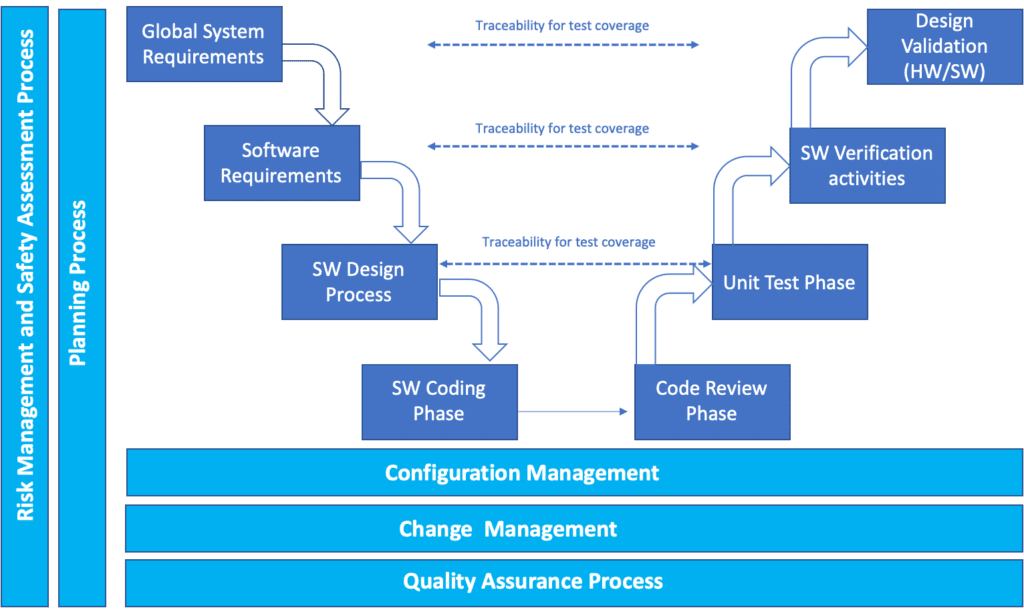
If, instead we take in consideration a general hardware device, Design Validation shall include, a part fulfilment of the identified user needs, testing activities related to the safety of the device according to its intended use, for example:
- Biocompatibility Evaluation
- Electrical Safety and Electromagnetic Compatibility, in case of active device
- Packaging Validation / Sterilization Validation
- Usability
- Clinical Investigation
It is essential to have a traceability between user needs/ system requirements and validation tests used to demonstrate fulfilment of that specific requirements. This can be performed through the documentation of what we can call a “Design Matrix”, where the correlation between design inputs and outputs is documented, along with the method For example:
| User Needs (design inputs) | Design Outputs | Verification / Validation Test |
| The device shall be safe to be used on patients from biocompatibility point of view | Product Specification of the device, along with description of the materials | Validation activities related to compliance with ISO 10993 family of standard. |
Design verification as per FDA requirements
During the design process, design verification plays a crucial role in ensuring that the design outputs align with the design inputs. As previously discussed in the definition section, design verification involves the identification of specific requirements that pertain to the functionality, performance, usability, and safety of the device. This verification process aims to demonstrate that each of these identified requirements is effectively addressed.
To facilitate the design verification process, it is imperative to develop a comprehensive test plan for each specific requirement. These test plans outline the procedures and methodologies to be followed in order to validate and verify the design outputs. Additionally, thorough documentation in the form of test reports is essential to capture the results and outcomes of the verification activities, ensuring that all identified requirements are met and adequately addressed.
Unlike design validation, which focuses on the system-level evaluation, design verification encompasses testing activities at various stages of the design process. This means that verification activities can be conducted across multiple layers of the design, ensuring that each component and aspect of the design is thoroughly assessed. For example, considering the previously mentioned scheme, in the case of a Software as a Medical Device (SAMD), design verification encompasses activities such as code reviews, unit tests, and system verification tests.
Code reviews involve a meticulous examination of the software code to identify any potential errors, inefficiencies, or inconsistencies. This process ensures that the code adheres to established coding standards and best practices. Unit tests, on the other hand, focus on testing individual units or modules of the software to verify their functionality and performance in isolation. This helps identify any flaws or defects within the individual units before they are integrated into the larger system. Finally, system verification tests validate the overall functionality, performance, and interoperability of the entire system, ensuring that it meets the defined requirements and specifications.
By conducting design verification activities across multiple layers of the design process, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and ensure that the final design meets the desired objectives and requirements. This comprehensive approach to design verification helps identify and rectify any potential issues or shortcomings early on, leading to a more robust and reliable end product.
-
 Design Control Procedure€64,00
Design Control Procedure€64,00
Verification vs Validation
If we want to compare the characteristics of verification vs validation activities, let’s have a look to the table below:
| Verification | Validation |
| Scope: Design Outputs meet Design Inputs | Design meets user needs and intended us of the device |
| System, subsystem and unit testing. | Test focused at a system level |
| During development. | After Development |
| Can be performed on prototype devices | Shall be performed on the same devices as the ones that will go on the market, or equivalent devices |
| It is performed against specific requirements selected by owner of the design | It is performed agains the selected user needs and requirements established by international standards. |
-
 Design Control Package€169,00
Design Control Package€169,00
Specific FDA Requirements for Design Verification and Design Validation Activities
In order to fulfill the requirements for verification and validation activities, certain specific criteria must be met. Both verification and validation processes necessitate the inclusion of a comprehensive test plan that outlines the methods, acceptance criteria, and, notably, statistical techniques with a rationale for determining the sample size. This statistical justification is crucial to ensure that the number of samples tested is statistically significant and representative of the overall population.
Additionally, when it comes to design validation, there is another significant requirement pertaining to the selection of the sample type. As previously mentioned, ISO 13485:2016 states that design validation should be conducted on representative products, which may include initial production units, batches, or equivalent samples. The rationale behind choosing the specific product for validation purposes must be duly documented.
Similar to ISO standards, the FDA also has comparable requirements for design validation. It is evident that validation activities must be carried out on the final devices, and a clear justification for the chosen sample type must be provided. It is important to emphasize that this requirement applies to all forms of validation activities, including clinical validation.
By adhering to these guidelines and documenting the validation processes accordingly, manufacturers can ensure that their devices undergo rigorous and comprehensive testing. This approach helps to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards and fosters confidence in the safety, effectiveness, and reliability of the medical devices.
It is worth noting that validation activities play a crucial role in the overall product development lifecycle. They provide valuable insights into the performance and usability of the devices, identify potential risks or shortcomings, and validate that the devices meet the specified requirements and user needs. This includes evaluating the devices’ functionality, performance, safety, and overall quality.
Moreover, the use of statistical techniques in the verification and validation processes adds an additional layer of rigor and objectivity. By applying appropriate statistical methods, manufacturers can ensure that the sample size used in the tests is sufficient to draw statistically significant conclusions and make informed decisions about the device’s performance and compliance.
Furthermore, for clinical validation specifically, it is essential to conduct studies using representative patient populations and real-world scenarios. This helps to assess the device’s performance in actual clinical settings and verify its effectiveness and safety under various conditions. The data collected during clinical validation is crucial in supporting claims about the device’s intended use, therapeutic benefits, and risk mitigation measures.
Design Control Procedure
4EasyReg has prepared a Design Control Procedure ready to be downloaded that is fully compliant with the section 7.3 of ISO 13485:2016 and 21 CFR 820.30. The procedure provides a detailed list of documentation that is necessary to prepare to build the whole Design History File of a medical device, based on the different phases of the design process. Moreover, the procedure provides as well guidelines for specific documentation which are of fundamental importance for the design process, for example the design review, design and development plan or the list of applicable regulatory requirements associated to the device.
-
 Design Control Procedure€64,00
Design Control Procedure€64,00
Subscribe to 4EasyReg Newsletter
4EasyReg is an online platform dedicated to Quality & Regulatory matters within the medical device industry. Have a look to all the services that we provide: we are very transparent in the pricing associated to these consulting services.
Within our WebShop, a wide range of procedures, templates, checklists are available, all of them focused on regulatory topics for medical device compliance to applicable regulations. Within the webshop, a dedicated section related to cybersecurity and compliance to ISO 27001 for medical device organizations is also present.
As one of the leading online platforms in the medical device sector, 4EasyReg offers extensive support for regulatory compliance. Our services cover a wide range of topics, from EU MDR & IVDR to ISO 13485, encompassing risk management, biocompatibility, usability, software verification and validation, and assistance in preparing technical documentation for MDR compliance.
Do not hesitate to subscribe to our Newsletter!

