What is Process Validation?
Medical device process validation and the related IQ/OQ/PQ technique, is defined as the collection and evaluation of data, from the process design stage throughout production, which establishes scientific evidence that a process is capable of consistently delivering quality products; process validation is documented with validation protocol and a final validation report, along with a series of other documents that we’ll describe here below. The goal of process validation activities is ensuring quality, safety and efficacy of the finished product. The validation processes is a key requirements which is present in any type of regulation, from ISO 13485 to FDA or EU MDR 2017/745.
It is essential that process validation activities are fully integrated within the Quality Management System of the organization and that other QMS processes such as CAPA, design control and statistical techniques for sampling methodologies.
Example of processes that require validation are sterilization, cleaning, reprocessing, etc.
The Different Types of Process Validation
There are different types of process validation, that differs one to each other based at which stage of the production lifecycle the validation is performed. The different types of process validation are summarised in the scheme below.
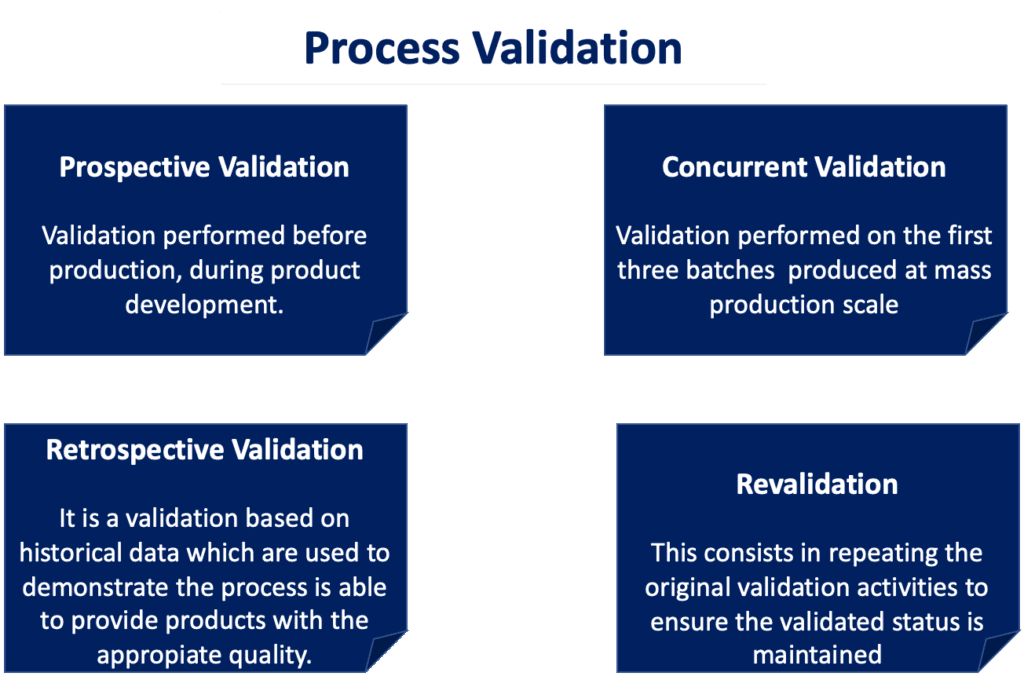
-
 Process Validation Procedure€64,00
Process Validation Procedure€64,00
Process Validation Protocol
The first document should be prepared when starting a process validation activities is the validation protocol. The protocol should be as much complete as possible and, at least, shall reference or provide information on the following topics, as per FDA requirements.
1) Identification of the process to be validated
The process under validation shall be identified and described. If it is a complex process constituted by multiple sub-process, all them should be described or at least referenced.
2) Identification of the medical devices manufactured using the process
The medical devices manufactured with process under validation shall be fully identified. The medical devices manufactured with process under validation shall be fully identified. Take always in consideration that process validation activities, like any other activities within the quality system, shall be performed using a risk-based approach. Thus the validation efforts shall be proportional with the associated risks on potential safety issue on the patient, user or any other person.
3) Objective and measurable criteria for a successful validation
The criteria for which the validation activities can be considered successful shall be fully described within the validation protocol. Basically, it is essential to identify the acceptability criteria for validation results and clearly identify what are the results to be met in order to consider the process validated.
4) Length and duration of the validation
The length and duration of the validation shall also be defined using a risk based approach, taking in consideration the potential risk on the end-user. A justification rationale shall be provided on the choice of length and duration of validation activities.
5) Operators, equipment to be used in the process
Opeators and equipment to be used during validation activities shall be identified. Note that:
- it is essential to ensure that the operators are trained on the process under validation and that this training is documented and included in the validation documentation.
- All the equipments shall be properly identified and calibrations shall be performed and documented, if needed.
As mentioned before, these are only some of the items to include in the validation protocol. There are much more (for example, specifications that relate to the product, components; product characteristics to be monitored; or statistical methods for data collection and analysis. For a complete and full description of what to include in a process validation protocol, refer to the Process Validation Procedure.
Methodologies for Process Validation: IQ, OQ and PQ
The standard approach for process validation is based on the so-called IQ,OQ,PQ technique. Let’s for each phase the definition defined by the FDA.
The Installation QualificationPhase (IQ) consists in ensuring by that all key aspects of the process equipment and ancillary system installation adhere to the approved specifications. The Operational Qualification (OQ) phase consists in establishing process control limits and action levels which result in product that meets all predetermined requirements. This basically is performed by performing operations at limits of the acceptability criteria for specific parameters and demonstrating that, even at the process limits, the output of the process is within the defined specifications. Finally, the Performance Qualification (PQ) consists in the demonstration that the process, under anticipated conditions, consistently produces a product which meets all predetermined requirements.
Let’s now see each of this phase more in details.
Installation Qualification (IQ)
Installation Qualification (IQ) is the first step for a process validation activity. It includes the verification that all the utilities and equipment have been properly delivered, installed and configured according to the specification. It is often requires to fill in a specific checklist to demonstrate the the utilities or equipment is properly installed. If the tool or equipment has been received from a supplier, it is essential in this phase to ensure that all the documentation of the equipment such as Installation Manual and/or User Manual of the equipment.
Safety features sand related documentation shall also be considered during the IQ phase; moreover software documentation is needed if the equipment or tool contains a software part.
Operational Qualification (OQ)
This is the phase where worst case process-related settings shall be used to demonstrate the ability of the process to generate product within the defined requirements. The OQ phase can include process control limits, SW-related parameters, process SOP, training, potential failure modes, action levels and worst-case conditions, etc.
Performance Qualification (PQ)
In this phase, the process under standard operating conditions is evaluated to ensure it provides product within the defined requirements. It is essential that product stability and repeatibility of the process outcome are demonstrated within the PQ phase. All the possible variables that could influence the outcome of the process should evaluted and monitored during OQ and PQ phase.
Validation Report
At the end of the validation activities, a final report shall be prepared drawing conclusions on the overall results of the validation activities, providing as well a summary of the protocol and related results.
Subscribe to 4EasyReg Newsletter
4EasyReg is an online platform dedicated to Quality & Regulatory matters within the medical device industry. Have a look to all the services that we provide: we are very transparent in the pricing associated to these consulting services.
Within our WebShop, a wide range of procedures, templates, checklists are available, all of them focused on regulatory topics for medical device compliance to applicable regulations. Within the webshop, a dedicated section related to cybersecurity and compliance to ISO 27001 for medical device organizations is also present.
As one of the leading online platforms in the medical device sector, 4EasyReg offers extensive support for regulatory compliance. Our services cover a wide range of topics, from EU MDR & IVDR to ISO 13485, encompassing risk management, biocompatibility, usability, software verification and validation, and assistance in preparing technical documentation for MDR compliance.
Do not hesitate to subscribe to our Newsletter!
