In this article, we want to give you a deep dive into the requirements associated to the Design and Development Plan. As you know, the Design Process for medical devices can be quite complete, with a lot of interconnection between the different departments of the organisation. As we already discussed, the design process is documented through the so-called Design History File, a collection of documentation and records related to the different phase of the Design Process. If we use the classic V-cycle to represent the different phase of the design process, the design plan represents the first step. It is important to mention that we are talking about the planning for the overall Design Process, and not about the Software Development Plan, which is a specific requirements related to the IEC 62304.
In this article, we will give a broad overview of the requirements of the Design and Development Plan, mainly focusing on three different regulations:
- ISO 13485:2016 standard
- 21 CFR 820 – FDA Quality System Regulations
- MDSAP – Medical Device Single Audit Program
Design and Development Plan Requirements According to ISO 13485:2016
The ISO 13485:2016 standard outlines specific requirements for the Design and Development Plan, which can be found in section 7.3.2. This plan serves as a vital tool for effectively controlling the design process, ensuring its adherence to regulatory and quality standards. It is important to note that the Design Plan should be continuously updated throughout the entirety of the design process.
To provide clarity on the essential components of the Design and Development Plan, the ISO 13485:2016 standard presents a comprehensive framework.
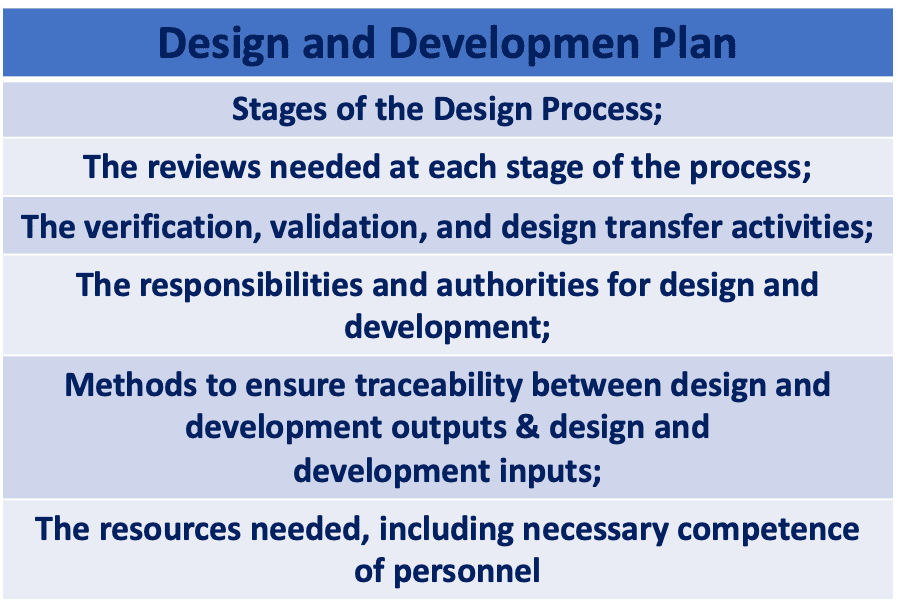
Stages of Design and Development
Within this section of the Design and Development Plan, it is crucial to incorporate the various milestones that mark the progression of the design process. These milestones encompass key stages starting from the initial conception and prototyping phases, leading up to the final release of the devices onto the market, following successful completion of the development process.
The Design and Development Plan should provide a comprehensive overview of these milestones, outlining the specific activities and objectives associated with each stage. This helps ensure a systematic and well-structured approach throughout the design process. By clearly defining the milestones, the plan enables effective project management and facilitates timely decision-making.
Additionally, it is essential to emphasize the collaborative nature of the design process, highlighting the interactions among different departments within the organization. The success of the design process relies on seamless coordination and cooperation between various departments, including Research and Development (R&D), Quality Assurance, Marketing, and Purchase & Supplier Management.
The R&D department plays a central role in driving the design process, leveraging their expertise and technical knowledge to develop innovative and effective solutions. They are responsible for translating conceptual ideas into tangible designs and prototypes.
The Quality Assurance department ensures that the design process adheres to regulatory requirements and internal quality standards. They contribute by conducting risk assessments, implementing quality control measures, and performing audits to verify compliance.
The Marketing department provides valuable input by identifying user needs, market trends, and customer preferences. Their insights help shape the design specifications, ensuring that the final product meets the expectations and requirements of the target market.
The Purchase & Supplier Management department plays a critical role in sourcing necessary components, materials, and services from suppliers. Their involvement in the design process ensures the availability of high-quality resources and fosters effective supplier relationships.
By acknowledging the contributions of these departments and promoting effective collaboration, the Design and Development Plan establishes a framework for cross-functional teamwork. This synergy enables the organization to leverage the diverse expertise and perspectives within the organization, resulting in a robust and well-rounded design process.
Design Review Needed at each stage of the process
During the progression of the design process, a crucial step that must be undertaken is the Design Review. This pivotal phase involves a comprehensive evaluation of the outcomes achieved thus far in the design process. It serves as a platform for decision-making and enables the team to determine the next steps in accordance with the Design Plan. In order to ensure an organized and efficient review process, it is imperative to clearly outline in the Design Plan the specific stages at which these reviews will take place.
The Design Review holds significant importance as it enables the project team to assess the progress made during each stage of the design process. This comprehensive evaluation encompasses various aspects, including design specifications, functionality, safety considerations, regulatory compliance, and overall alignment with the desired outcome. By conducting these reviews at predefined intervals, the team can systematically evaluate the design’s performance and identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
In the Design Plan, it is crucial to specify the precise stages or milestones within the design process at which the Design Reviews will be conducted. This ensures that the review process aligns with the project timeline and allows for timely decision-making. The identified stages may include key junctures such as the completion of initial concept designs, prototype development, verification and validation activities, and finalization of the design prior to market release.
By incorporating the Design Review stages into the Design Plan, the project team gains clarity and a shared understanding of when critical assessments will take place. This proactive approach facilitates effective communication and collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and relevant departments. It allows for informed decision-making, enabling prompt adjustments or modifications to the design, if necessary, to ensure compliance with established requirements and goals.
Furthermore, documenting the Design Review stages in the Design Plan fosters transparency and accountability within the design process. It provides a clear framework for tracking progress, identifying potential bottlenecks, and assigning responsibilities. This level of clarity and structure helps to minimize the risk of overlooking important design considerations and promotes a robust and iterative approach to design development.
-
 Design Review Template€64,00
Design Review Template€64,00
Verification, Validation and Design Transfer.
As discussed in some previous posts in the QualityMedDev website, verification, validation and design transfer are key phases of the Design Process. It is necessary to define, in the Design and Development Plan, the activities related to verification and validation necessary in the specific stage of the process. If the device is constituted by hardware and software, this shall be reflected into the design plan and the activities for software verification and validation shall be included.
Responsibilities and Authorities
It is very important that responsibilities for the different phases and activities of the design process are documented in the Design and Development Plan. It is essential to have documentation fully aligned between the responsibilities mentioned din the Design and Development Plan and the related Job Description and trainings associated to the personnel involved in the Design Process.
Traceability through the Design Process
One of the key requirements in the design process is establishing traceability between design inputs and design outputs. This traceability ensures a clear link between various elements and facilitates effective management of the design process. To accomplish this, organizations often utilize a valuable tool known as the Design Traceability Matrix.
The Design Traceability Matrix serves as a comprehensive document that establishes connections between different components, including design inputs, design outputs, associated risks, and verification activities. By utilizing this matrix, organizations can systematically track and maintain traceability throughout the design process, ensuring that all design requirements are adequately addressed and verified.
In the matrix, the Design Inputs section outlines the specific requirements and criteria that serve as the foundation for the design process. These inputs can encompass a wide range of factors such as performance specifications, user requirements, regulatory standards, and safety considerations.
On the other hand, the Design Outputs section includes the tangible outcomes of the design process, such as product specifications, design drawings, technical documentation, and any other deliverables. These outputs should align with and fulfill the identified design inputs, ensuring that the intended product or device meets the desired requirements.
Furthermore, the Traceability Matrix also incorporates the aspect of risk management, as mandated by ISO 14971. It establishes the link between identified risks, the corresponding risk control measures, and the verification activities conducted to validate those measures. This comprehensive approach ensures that all risks associated with the design are adequately addressed and controlled throughout the development process.
Maintaining traceability through the Design Process, as documented in the Traceability Matrix, helps organizations effectively manage and monitor the progress of the design activities. It enables stakeholders to assess the completeness and consistency of the design, identify any gaps or inconsistencies, and make informed decisions based on the established connections.
-
 Traceability Matrix Template€64,00
Traceability Matrix Template€64,00
Resources Needed
The need of resources for the design process shall be mentioned in the Design and Development Plan. This section requirements shall be covered as well in the section related to “Responsibilities and Authorities”.
Design and Development Plan according to FDA regulation
As we know, FDA Quality System Regulations specifies the requirements related to Design and Development in the section 21 CFR 820.30. Specifically, 21 CFR 820.30 (b) contains the requirements for the design and development plan. The text of this part of the regulation is reported below:
Each manufacturer shall establish and maintain plans that describe or reference the design and development activities and define responsibility for implementation. The plans shall identify and describe the interfaces with different groups or activities that provide, or result in, input to the design and development process. The plans shall be reviewed, updated, and approved as design and development evolves.
As you can see, there is no much differences with the requirements mentioned in the ISO 13485:2016 and the two regulations are very similar. Basically, we can say that by preparing a Design and Development Plan compliant with ISO 13485:2016, we will automatically cover the requirements associated to 21 CFR 820.30 (b).
MDSAP Requirements for Design and Development Plan
When it comes to the MDSAP (Medical Device Single Audit Program) regulation, there are no significant additional requirements related to the Design and Development Plan beyond what has already been outlined in the ISO 13485 standard. The MDSAP program, which aims to harmonize regulatory requirements for medical devices across participating countries, does not introduce any specific amendments or supplementary criteria for the Design and Development Plan.
However, it is worth noting that certain countries such as Australia and Canada have their own specific guidelines and regulations in place. In these countries, the Design and Development Plan may be incorporated as part of the broader Quality Plan. This approach streamlines the documentation process and ensures that all necessary aspects are addressed within a single plan.
Notably, Health Canada, the regulatory authority in Canada, mandates that the Design and Development Plan be included as a specific requirement for Class IV medical devices. This emphasizes the importance of a well-documented and comprehensive plan for high-risk devices.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the Design and Development Plan holds significant importance in the design process of medical devices. Throughout this article, we have discussed the key requirements related to the design plan as outlined in various medical device regulations and ISO standards.
It is crucial to emphasize that the Design and Development Plan is a dynamic document that necessitates continuous updates throughout the entire design process. Auditors conducting assessments and inspections expect to observe tangible evidence demonstrating that the plan has been regularly modified and revised to accurately reflect the progress of the design activities.
By maintaining an updated Design and Development Plan, medical device manufacturers can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and demonstrate their commitment to effective design control. This document serves as a roadmap, guiding the design team and facilitating effective communication between different departments involved in the design process.
Additionally, the Design and Development Plan supports risk management activities by providing a framework for traceability between design inputs, design outputs, associated risks, and the verification activities employed to validate specific requirements and mitigate identified risks.
Design Control Procedure
QualityMedDev has prepared a Design Control Procedure ready to be downloaded that is fully compliant with the section 7.3 of ISO 13485:2016 and 21 CFR 820.30. The procedure provides a detailed list of documentation that is necessary to prepare to build the whole Design History File of a medical device, based on the different phases of the design process. Moreover, the procedure provides as well guidelines for specific documentation which are of fundamental importance for the design process, for example the design review, design and development plan or the list of applicable regulatory requirements associated to the device.
-
 Design Control Procedure€64,00
Design Control Procedure€64,00
Design and Development Package
4 EasyReg has developed a full package of templates, procedures and other documentation ready to be used for the implementation or the improvements of your design and development process, an essential steps to reach an adequate level of regulatory compliance.
The Design Control Package includes the following documentation:
- Design Control Procedure
- Design & Development Plan Template
- Design Inputs Template
- Design Review Template
- Design Verification Plan Template
- DHF Index Template
- DMR Index Template
- Design Transfer Checklist
Do not hesitate to click on the link below for a full description of the package:
-
 Design Control Package€169,00
Design Control Package€169,00
Subscribe to 4EasyReg Newsletter
4EasyReg is an online platform dedicated to Quality & Regulatory matters within the medical device industry. Have a look to all the services that we provide: we are very transparent in the pricing associated to these consulting services.
Within our WebShop, a wide range of procedures, templates, checklists are available, all of them focused on regulatory topics for medical device compliance to applicable regulations. Within the webshop, a dedicated section related to cybersecurity and compliance to ISO 27001 for medical device organizations is also present.
As one of the leading online platforms in the medical device sector, 4EasyReg offers extensive support for regulatory compliance. Our services cover a wide range of topics, from EU MDR & IVDR to ISO 13485, encompassing risk management, biocompatibility, usability, software verification and validation, and assistance in preparing technical documentation for MDR compliance.
Do not hesitate to subscribe to our Newsletter!

