The PDCA cycle stays at the base of any quality management system and it is an extremely important approach useful to fully understand the general structure of a quality system, independent from the type of business or type of industry it is related to.
In fact, the PDCA cycle can be related to multiple ISO standards, such us the well known ISO 13485 or ISO 9001, but as well to other more specific standards such us ISO 45001 or ISO 19011, among the others.
In this article we will discuss in depth the PDCA cycle and provide examples of the link to this PDCA approach with elements of any quality system.
The PDCA cycle was popularized Dr. W. Edwards Deming in the 1950s who coined the term “Shewhart” Cycle after his mentor. It was Deming who realized the PDCA Cycle could be used to improve production processes in the United States during World War II.
The PDCA Cycle
The PDCA approach is well defined in the introduction (Section 0) of the ISO 9001 version 2015 but it obviously can be applied to ISO 13485. Moreover, since a certified quality system is essential for CE marking, this approach could definitely be useful for MDR 2017/745 and IVDR 2017/746. As it is reported in the section of this standard, this approach can be applied to whatever type of process within an established quality system, as it provides a general framework that whatever type of process may follow.
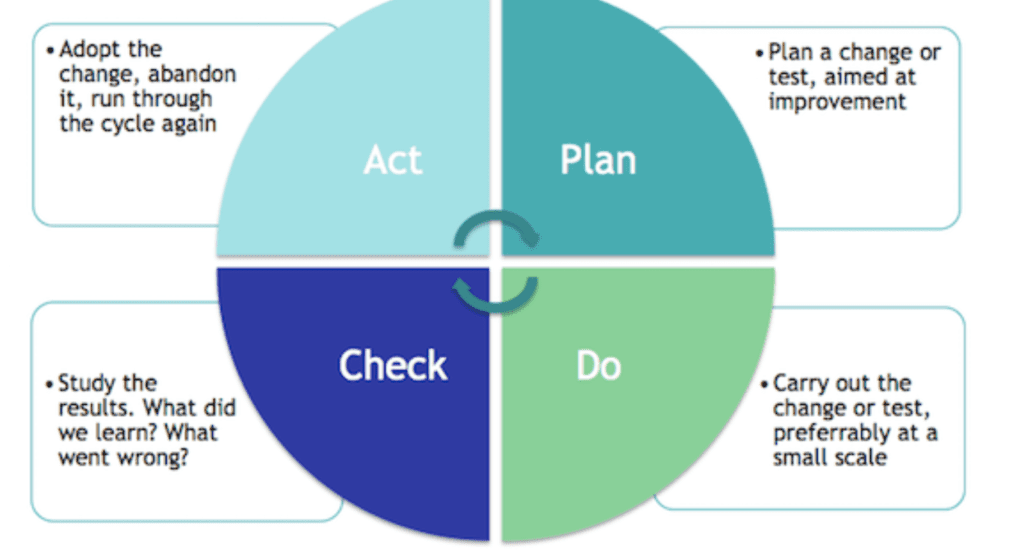
The PDCA can be summarised based on the following considerations:
- Plan: the first step is the planning phase. This consists on the establishment of the objectives of the system and its processes, based on customer requirements and internal organization policies.
- Do: this phase is related to the implementation of the plan
- Check: this is the phase where monitoring activities need to be performed, in order to check if the implementation phase was successful and the plan has been fully implemented.
- Act: if during the monitoring phase, any actions to further improve performance is identified, this needs to be Implemented.
PDCA and Process Approach
The key characteristic of any quality system is the so-called process approach. Basically, any process is based on inputs and outputs; the real process activities are the ones able to transform the inputs in outputs.
During the transformation from inputs to outputs, there might be some control points where the process is checked to ensure no deviations are highlighted.
Once again, the process approach is a general characteristics of any quality system process, independently from the type of management system and from the related business (medical device, automotive, safety, etc).
The management review is the key moments where control of the quality system processes can be performed and decisions on possible actions can be taken, if deemed necessary.
The Risk Based Approach
One of the key characteristics of quality management systems, especially the ones based on ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 is the so-called risk based approach.
Taking for example the ISO 9001, it is clear in section 0.3.3 that the organisations needs to evaluate risks and opportunities. Addressing both risks and opportunities is considered as the main starting point for improvement of the overall quality system.
One of the key process related to the implementation of the risk-based thinking is the preventive action process.
Process Improvements and the PDCA cycle
The PDCA process is similar to the so-called Kaizen method, which basically means “change for the better” or “continuous improvement.” Kaizen is where all employees are involved in improving productivity by finding efficiencies in the work environment. Like the PDCA cycle, Kaizen aims for continuous improvement through small, incremental changes.
Examples of changes that might be made through Kaizen or PDCA are using new systems, eliminating waste, or implementing just-in-time delivery. Not all changes need to be small or incremental.
The culture of the organisation plays a fundamental role both with Kaizen and PDCA method. In fact, the PDCA cycle tests employees’ ideas, adjusts them, and then implements them if they have potential. The cycle is an iterative process that continually tests concepts and promotes improvements.
Subscribe to 4EasyReg Newsletter
4EasyReg is an online platform dedicated to Quality & Regulatory matters within the medical device industry. Have a look to all the services that we provide: we are very transparent in the pricing associated to these consulting services.
Within our WebShop, a wide range of procedures, templates, checklists are available, all of them focused on regulatory topics for medical device compliance to applicable regulations. Within the webshop, a dedicated section related to cybersecurity and compliance to ISO 27001 for medical device organizations is also present.
As one of the leading online platforms in the medical device sector, 4EasyReg offers extensive support for regulatory compliance. Our services cover a wide range of topics, from EU MDR & IVDR to ISO 13485, encompassing risk management, biocompatibility, usability, software verification and validation, and assistance in preparing technical documentation for MDR compliance.
Do not hesitate to subscribe to our Newsletter!
